Ok, let's move on to what we did in class yesterday. Look down below for what we learned..... plus see some additional cool stuff under the info!
˜Chemical Bonding
- Chemical bonds happen when electrons from one atom are attracted by the nucleus of another atom. - There are three types of chemical bonds:
Nonpolar Covalent Bond = electrons are shared equally.
Polar Covalent Bond = electrons are shared unequally.
Ionic Bond = electrons are transferred between two atoms.
˜Electrostatic Force
- Opposite charges attract each other.
- Like charges repel each other.
- The greater the distance = the smaller the attractive force.
- The greater the charge = the greater the force of attraction.
- Electrostatic force is a force that exists between charged particles as a result of attraction or repulsion. This force goes in all directions.
˜Ionic Bonds
- Metals tend to lose their electrons, then nonmetals gain these electrons. Note that these electrons are transferred, not shared.
- When nonmetals lose electrons = positively charged ions (cations).
- When metals gain electrons = negatively charged ions (anions).
- Cations attract anions, and vice versa. This refers to an electrostatic attraction.
- Ionic bonds are very strong and an enormous amount of energy would be needed to break them apart. These ionic compounds also have high melting tempatures.
- Electronegativity = the measure of the tendency of an atom to attract electrons from a neighbouring atom.
- In general,
Metals = low electronegativity values.
Nonmetals = high electronegativity values.
- The scale that is used to measure electronegativity is called the Pauling Scale. The scale goes from 0.7 to 4.0.
- High electronegativity values equals to high ionization energy.
- To calculate an electronegativity difference:
ENeg Diff. = |ENeg1 - ENeg2|
1) If ENeg Diff. <0.5
It is a non-polar covalent bond.
2) If ENeg Diff. = 0.5 and = 1.8
It is a polar covalent bond.
3) If ENeg Diff. >1.8
It is an ionic bond.
˜Nonpolar Covalent Bonds
- When two atoms have less than full shells are able to share to attain a full electron shell.
- Nonpolar covalent bonds are very strong and an enormous amount of energy would be needed to break them apart.
- Some compunds have negative melting points which would be: CH4, O2, F2.
- Intramolecular Forces = found within a molecule, responsible for holding the atoms of a molecule together.
- Intermolecular Forces = between the molecules, responsible for the bonding between molecules.
˜Polarity
- Describes a molecule's electrical balance.
- If there is an imbalance with electrical charge, than a molecule is polar.
- If the electrical charge is the same strentgh, then it is nonpolar.
˜Polar Covalent Bonds
- Electronegativity difference. (refer to above)
- the atom with higher electronegativity = partial  (negative) charge.
(negative) charge.
 (negative) charge.
(negative) charge.- the atom with lower electronegativity = partial  (positive) charge.
(positive) charge.
 (positive) charge.
(positive) charge.˜Images, Videos, Worksheets
Images




 Ionic Bonding
Ionic Bonding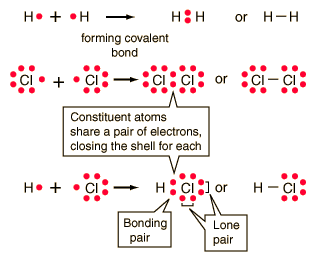
 Polar Covalent Bonding
Polar Covalent Bonding Polar Covalent Bonding
Polar Covalent Bonding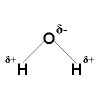 Polar Covalent Bonding
Polar Covalent Bonding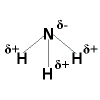 Polar Covalent Bonding
Polar Covalent Bonding Polar Covalent Bonding
Polar Covalent Bonding Ionic Bonding
Ionic Bonding Ionic Bonding
Ionic Bonding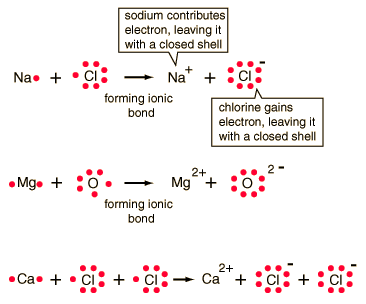 NOTE: Shows Valance Electrons!
NOTE: Shows Valance Electrons! Sodium Chloride Crystal Structure
Sodium Chloride Crystal StructureVideos
Worksheets
4) http://schools.bibb.k12.ga.us/16542091810856967/lib/16542091810856967/ChemicalBondingWorksheet.pdf
Ok, well I am done for today. Everyone enjoy your long weekend!!!! :)
No comments:
Post a Comment