FUNCTIONAL groups, that is! Functional groups are bunches of particles that exhibit the same characteristics in reactions.
The four main ones we'll be looking at are:
- HALIDES/ NITRO COMPOUNDS
- ALCOHOLS
- ALDEHYDES
- KEYTONES
HALIDES/ NITRO COMPOUNDS
Let's start with halides and nitro compounds.
Halides can also considered to be insoluble in water. Teflon, a halide compound, tends not to react with other chemicals, while iodine can produce a bigger reaction.
Naming: find the main chain name, and add the following prefixes:
F=fluoro
Cl= chloro
Br= bromo
I= iodo
NO2= nitro
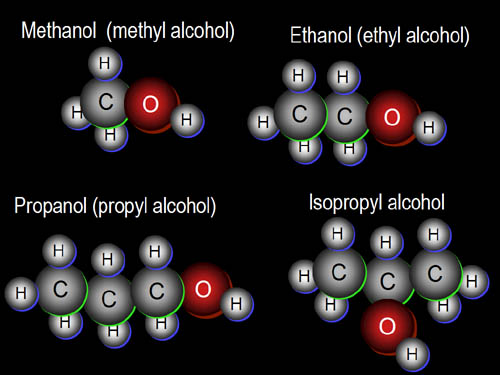
ALCOHOLS
Some characteristics: alcohols tend to have a high boiling point. The solubility of alcohols depends on the chains that make it up. The longer and more complicated the chain, the more insoluble it is. Alcohols tend to be liquids at room temperature.
Naming: naming alcohols is easy. Find the longest main chain with the OH group, and drop the "e" off at the end. Add on an "ol".
ALDEHYDES AND KEYTONES
Naming: for aldehydes, drop the "e" of the parent chain and add "al". For keytones, drop the "e" and add "one".